Bandicam settings - Audio only
The 'Audio' tab allows users to set Audio-only hotkey and format settings.
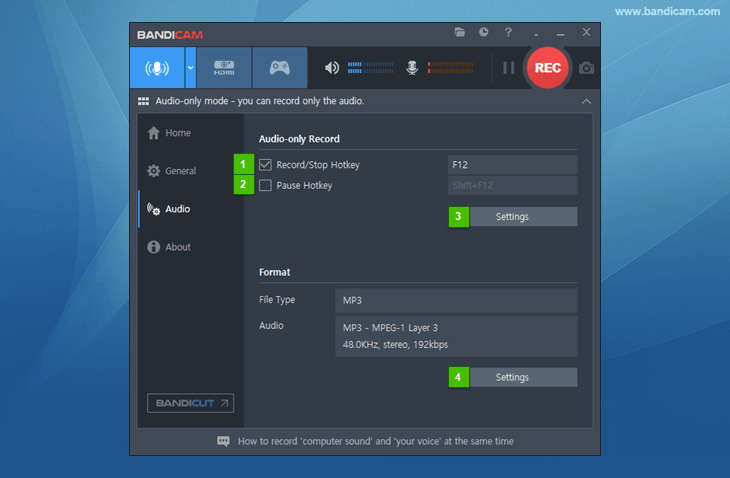
- Record/Stop Hotkey: The hotkey for the 'Record/Stop' functions can be set.
- Pause Hotkey: The hotkey for the 'Pause' function can be set.
- Audio-only Record Settings: This button allows users to set the speaker/microphone device selection, microphone volume control, and noise suppression filter.
- Format Settings: This button allows users to set the file extension (MP3 or WAV), audio channels, frequency, and bitrate.
*** The [Audio] tab can only be seen when you select the "Audio Only" recording menu.
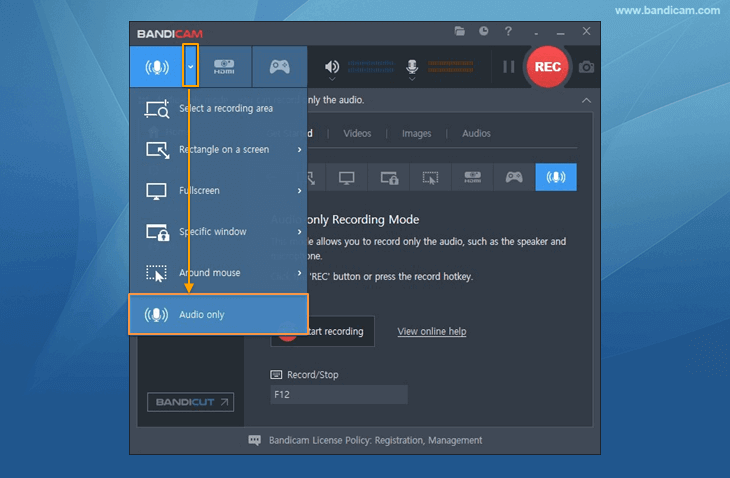
Audio-only Record settings
The Audio-only Record settings window allows users to set the speaker/microphone device selection, microphone volume control, and noise suppression filter.
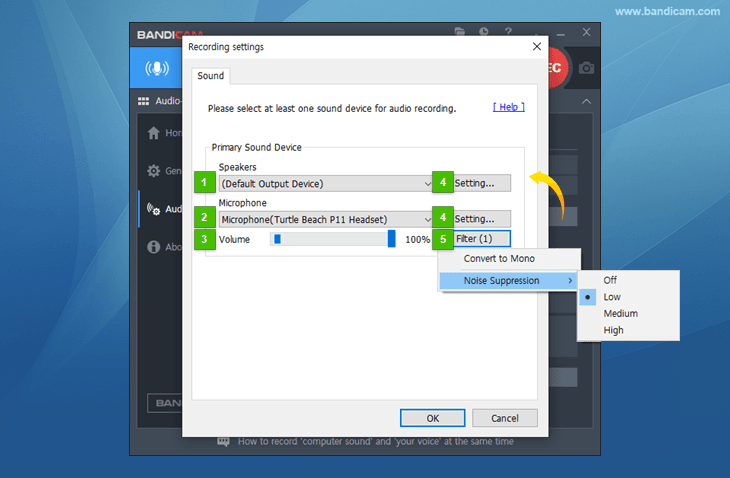
- Speakers (Primary Sound Device): This allows users to select a device for recording computer sound.
- Microphone (Primary Sound Device): This allows users to select a device for recording microphone sound.
- Volume: If you select a microphone device, you can set the volume of the microphone to record.
- Settings: This button allows users to open the [Playback] or [Recording] settings of Windows.
- Filter: This option allows users to use the microphone filter function.
- Convert to Mono: The microphone input is converted from Stereo to Mono.
- Noise Suppression: This allows you to record microphone sounds by reducing external noise, such as mouse clicks and keyboard sounds.
Recording format settings
The Format settings window allows users to set the file extension (MP3 or WAV), audio channels, frequency, and bitrate.
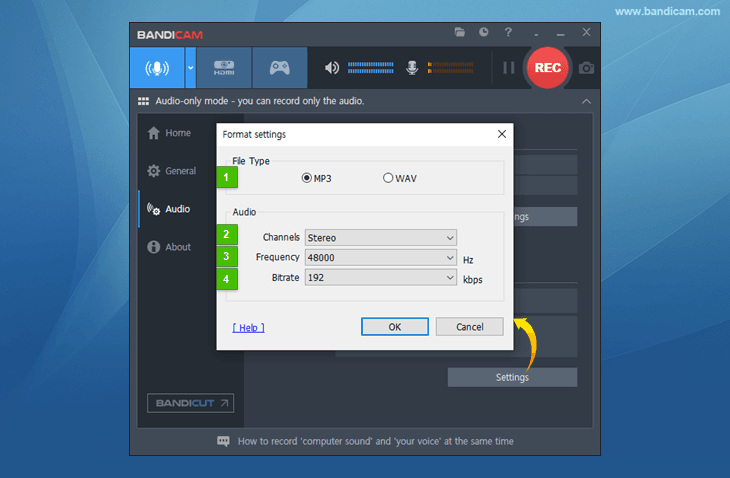
-
File Type
- MP3: MP3 (MPEG-1 L3) is one of the most popular audio codecs. MP3 files use lossy compression, which compacts audio drastically, and MP3 is generally more efficient than MP2 at the same bitrate.
- WAV: This is a file extension that saves uncompressed files without loss of sound quality.
-
Audio - Channels
- Stereo: Stereo sound is usually achieved by using two or more independent audio channels. It is used in most entertainment applications.
- Mono: Mono sound is single-channel. It is used for radiotelephone communications, telephone networks, etc.
-
Audio - Frequency (Hz) Also known as the sampling rate, frequency is the number of samples per second.
- 22,050 Hz: Used for lower-quality PCM and MPEG audio
- 32,000 Hz: Used for television sound in some countries
- 44,100 Hz: Used for Audio CDs, also most commonly used with MPEG-1 audio (VCD, SVCD, MP3)
- 48,000 Hz: The standard audio sampling rate used by professional digital video equipment
-
Audio - Bitrate (kbps) Bitrate represents the amount of information.
- 96-128 kbps: FM radio quality
- 192 kbps: Near CD quality
- 256 kbps: CD quality
- 320 kbps: The highest quality MP3 bitrate is 320 kbps

